


7.2 Interne Ebene: Hashorganisation (eindimensional, dynamisch)
IF (sp==0) s = hlv(w);ELSE ¯{ s = hlv-1(w);
IF (s < sp) s = hlv(w);
}
Hashorganisation (eindimensional, dynamisch)
Ausnahme: erstes Splitten: lv = lv+1, sp=sp+1
Hashorganisation (eindimensional, dynamisch)
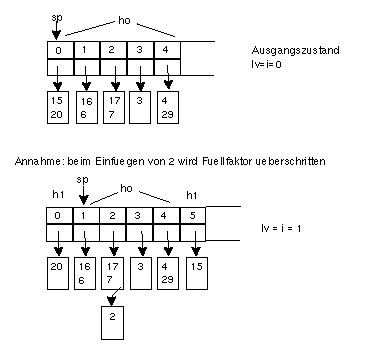
Beispiel: hi(w) = w mod 2i*5 (N=5)

h0(w) = w mod 20*5
h1(w) = w mod 21*5
Quicky: was passiert bei Suche nach 15, 20, 3, 2?
Nachteil des lin. Hasing: evtl. werden Seiten gespittet, die gar nicht voll sind


